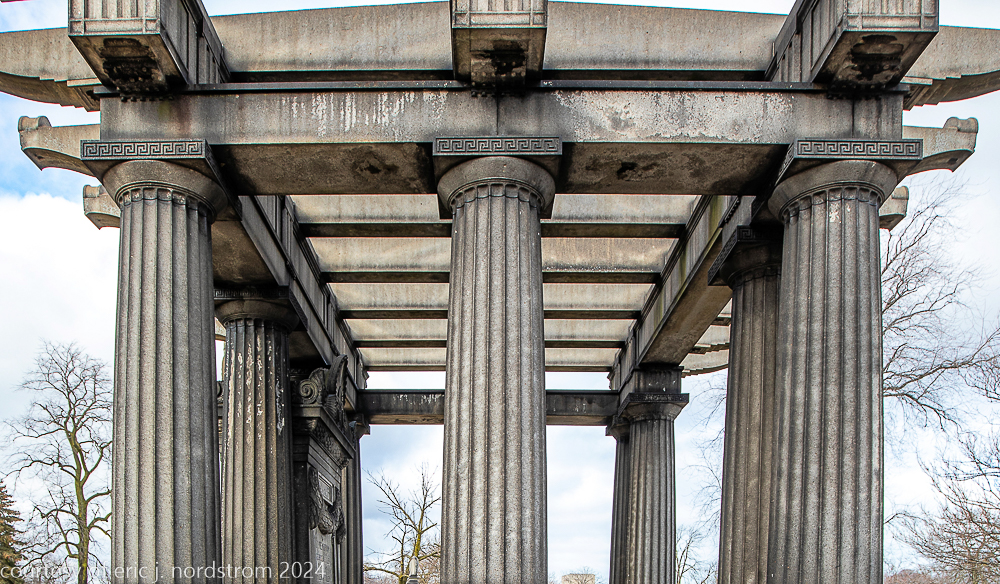
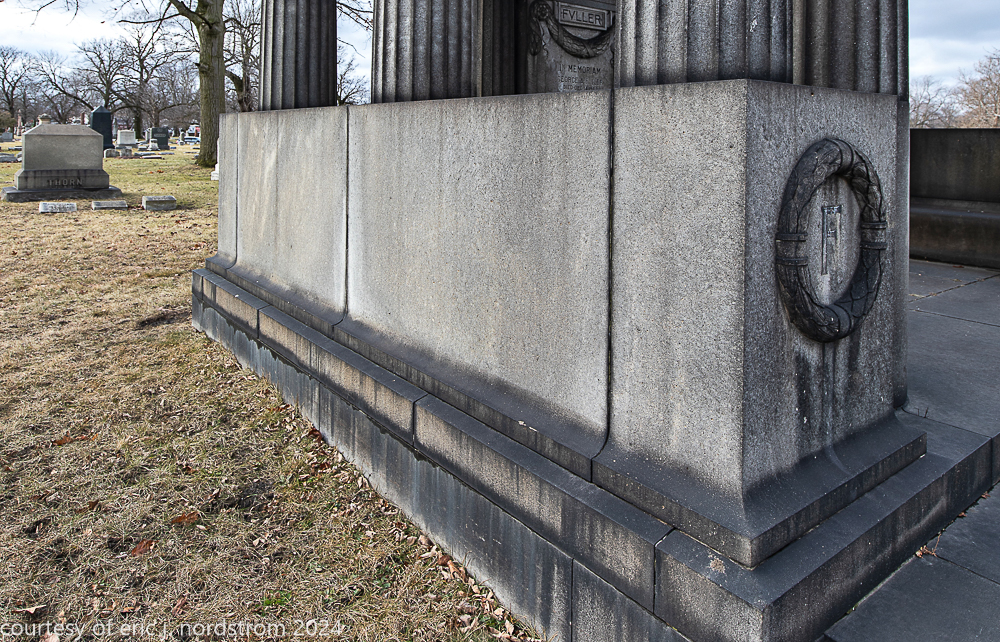
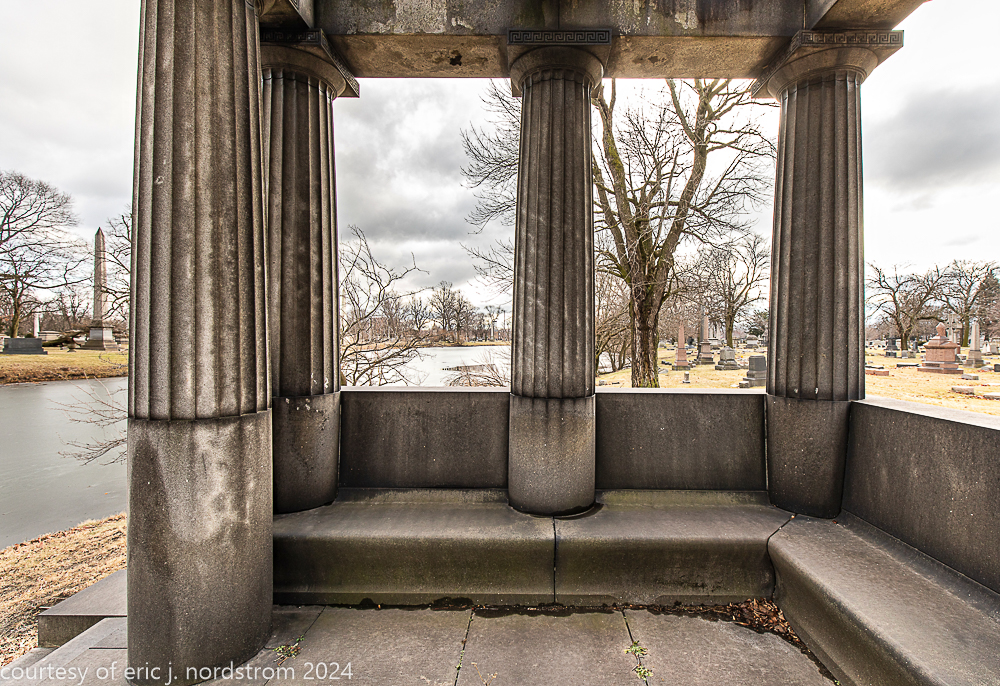
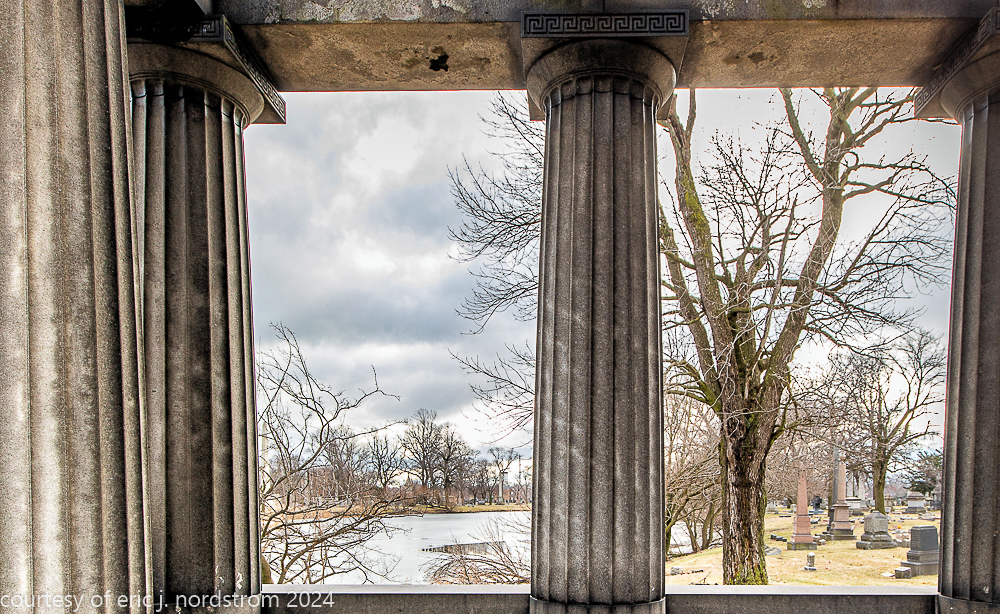
bruce price's eternal monument or "doric tomb" to skyscraper builder george a. fuller
This entry was posted on February 1 2024 by Eric
 George A. Fuller (October 21, 1851 – December 14, 1900) was an American architect often credited as being the "inventor" of modern skyscrapers and the modern contracting system.
George A. Fuller (October 21, 1851 – December 14, 1900) was an American architect often credited as being the "inventor" of modern skyscrapers and the modern contracting system.

Early life and career:
Fuller was born in Templeton, Massachusetts, near Worcester. After graduating from Andover College, he took a course in architecture at the Boston School of Technology and then started in the office of his uncle, J.E. Fuller, an architect in Worcester, Massachusetts. Fuller soon entered the office of Peabody & Stearns – a firm which specialized in building mansions for the rich in Newport, Rhode Island – where he soon developed a strong interest in the details of erecting a building, and was particularly interested in "skyscrapers", the name recently given to the tall buildings that had been made possible by Elisha Otis' invention of the safety elevator. At the age of twenty-five he was made a partner and placed in charge of Peabody & Stearns's New York office.
In New York, Fuller's design for a new club house for the Union League Club of New York, a Queen Anne mansion for the site at the corner of Fifth Avenue and 39th Street, won over eight other designs, including those submitted by noted architects Richard Morris Hunt and Charles McKim and William Rutherford Mead. Fuller also designed the United Bank Building, a nine-story building at Wall Street and Broadway, although he left Peabody & Stearns shortly after construction began, having spent four years there.
George A. Fuller Company:
Fuller moved to Chicago, the locus of much of the skyscraper construction in the United States at the time, where he formed a partnership with C. Everett Clark, another architect from Massachusetts, which lasted only two years. He then raised $50,000 and set up the George A. Fuller Company in 1882. Fuller's new firm was different from the many architecture firms of the time, in that it intended to handle all aspects of building construction except for the design of the building, which would come from outside architects. In this way, Fuller created the modern concept of the general contractor.
One of the new firm's first jobs was the Chicago Opera House, designed by Henry Ives Cobb and Charles S. Frost. In this building, Fuller, who was a proponent of using steel in building construction, utilized it for the floor beams, a decision which subjected him to criticism from the architectural community, which was wary of using steel and unsure of its long-term properties.
Very little is really known today of the properties of steel ... and though events point strongly to [it] becoming the metal of the future, there exists among many reasonable conservative men, a wide and well-grounded distrust of its use in the higher engineer or architectural structures, on account of its mysterious behavior, and frequent erratic and inexplicable failures.
Fuller's firm built the Tacoma Building in Chicago designed by Holabird & Roche and completed in 1889, which was the first skyscraper with non load bearing curtain walls. By using Bessemer steel beams, Fuller created steel cages that supported all the building's weight.
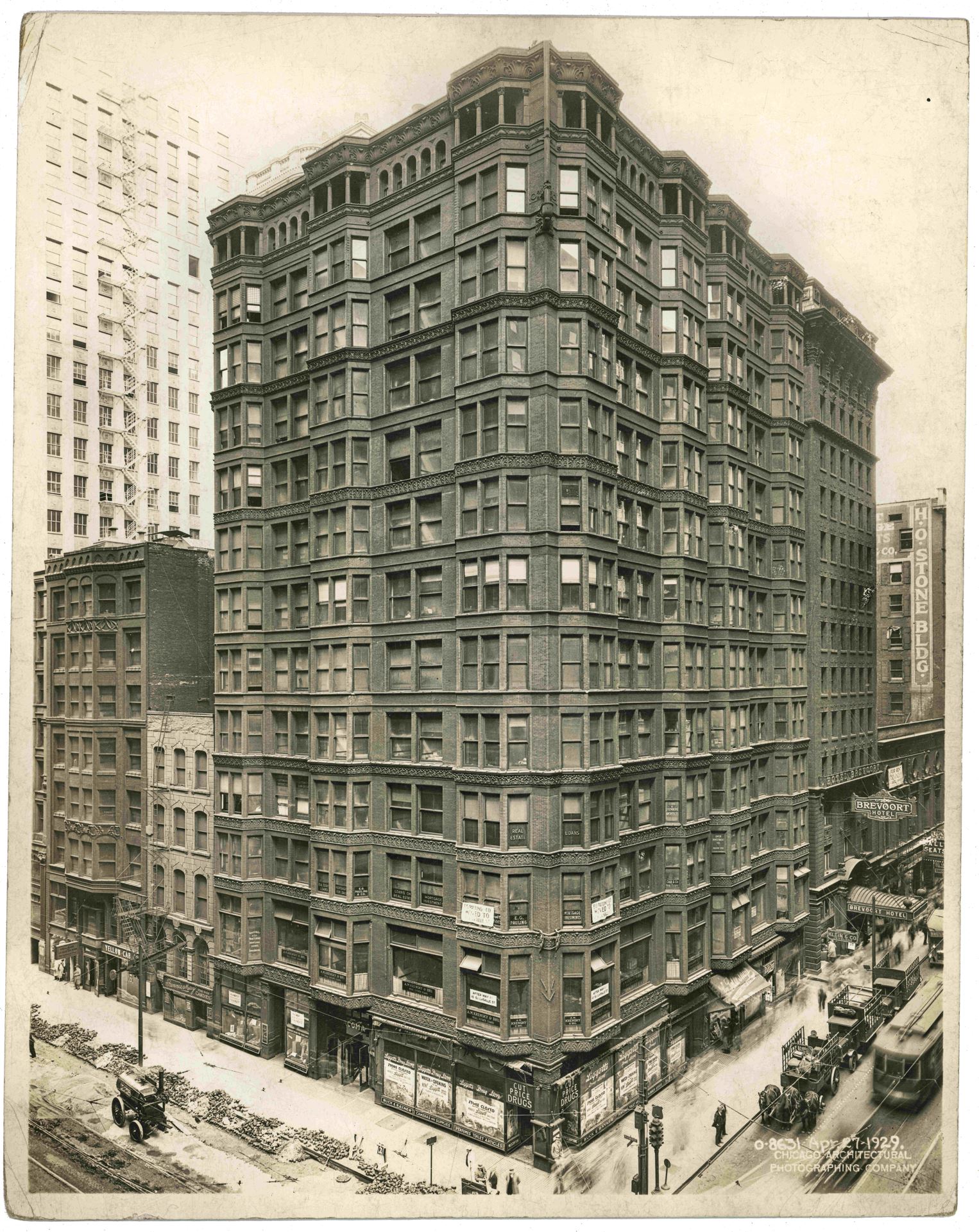

Fuller's firm also built the Rookery Building (1888, Burnham and Root), the Rand McNally Building (1890, Burnham & Root), the Pontiac Building (1891, Holabird & Roche) and the Monadnock Building (1891, Burnham & Root; 1893, Holabird & Roche) in Chicago, and the New York Times Building (1889, George B. Post) in New York City. The Fuller Company was also intensely involved in the building of the Chicago World's Fair of 1893, the Columbian Exposition, in which a temporary "White City on the Lake" was constructed under the supervision of Daniel Burnham.
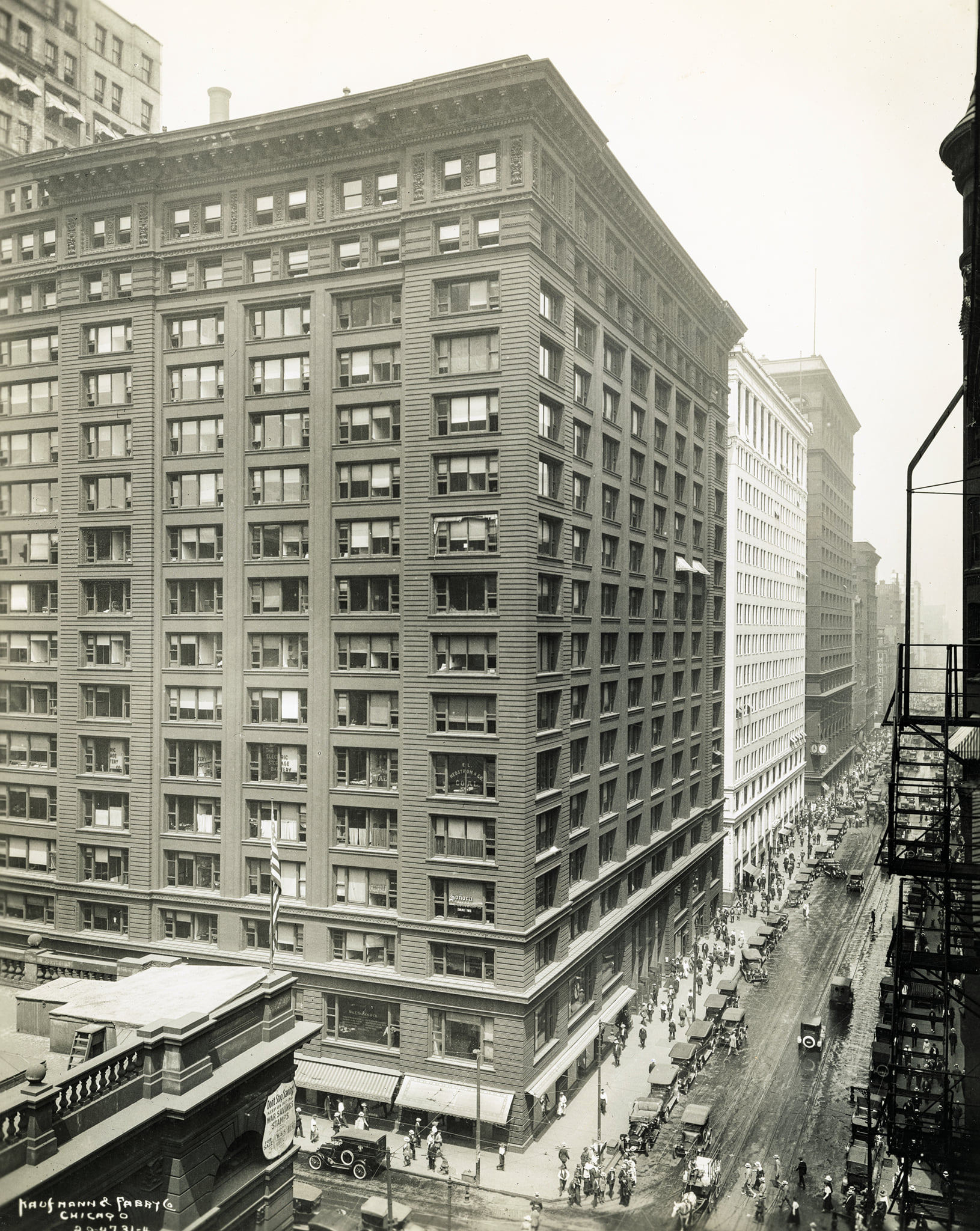

With the success of his firm, Fuller became a multimillionaire, and his wife and daughters entered Chicago society. He commissioned Charles P. Post to design a home on Drexel Boulevard on the South Side of Chicago, and Post created a Queen Anne style mansion. His daughter, Allon, married Harry St. Francis Black in 1894, and Fuller took him into the company as vice president, despite the fact that Black was neither an architect nor an engineer.
In 1892, New York City altered its building regulations to allow skeleton construction and curtain walls, in which the load created by the building was carried by the internal skeleton and not by the exterior wall, a construction method which had been allowed under the Chicago building code for years. This change prompted Fuller to open an office in New York in 1896, and soon the company had contracts in Boston, Pittsburgh, St. Louis and Baltimore, as well as in Chicago and New York. Future skyscraper builder William A. Starrett joined the company in 1897 as an office boy.
Death
Fuller died suddenly on December 14, 1900, from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, leaving an estate valued at $3 million. His tomb at Oak Woods Cemetery in Chicago, designed by New York architect Bruce Price, is one of the largest in the cemetery.
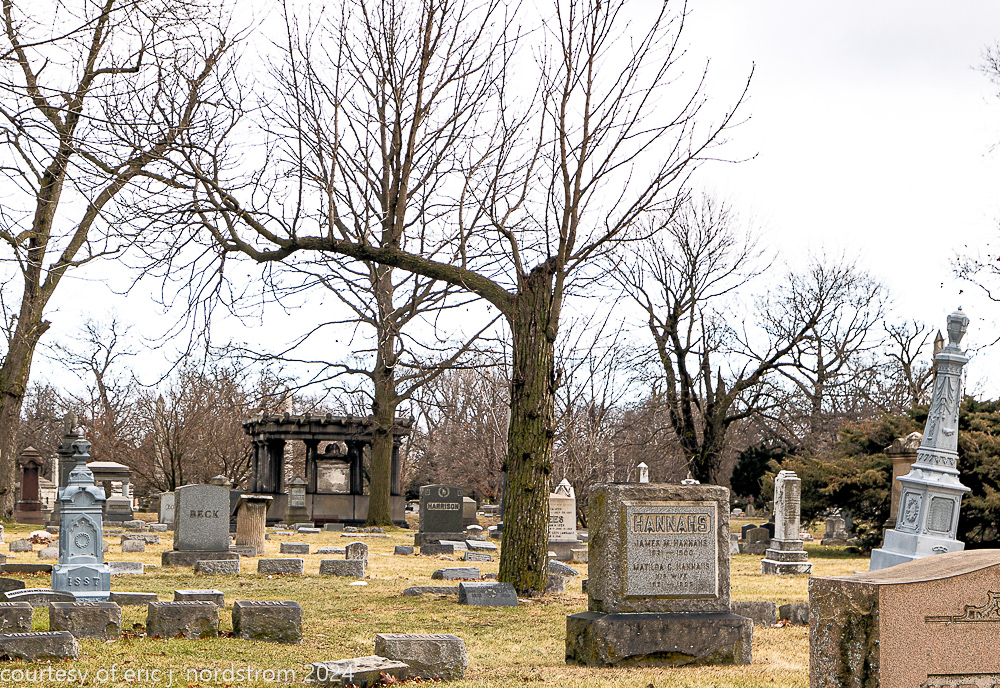
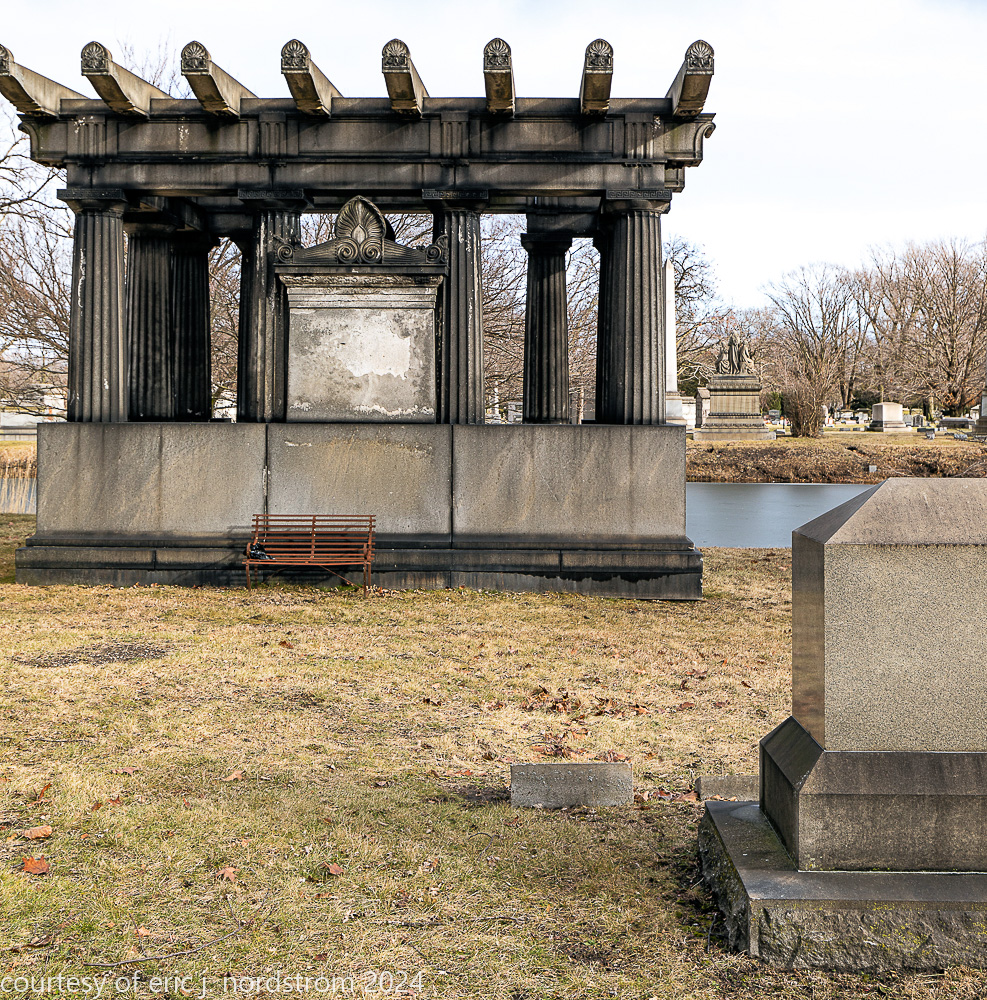
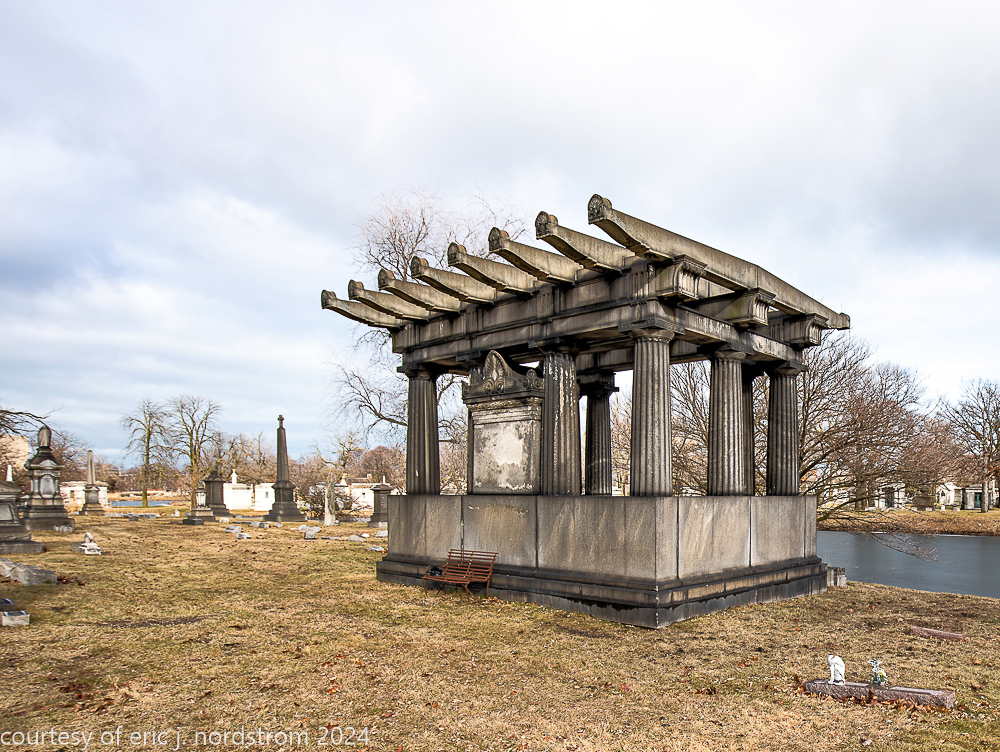
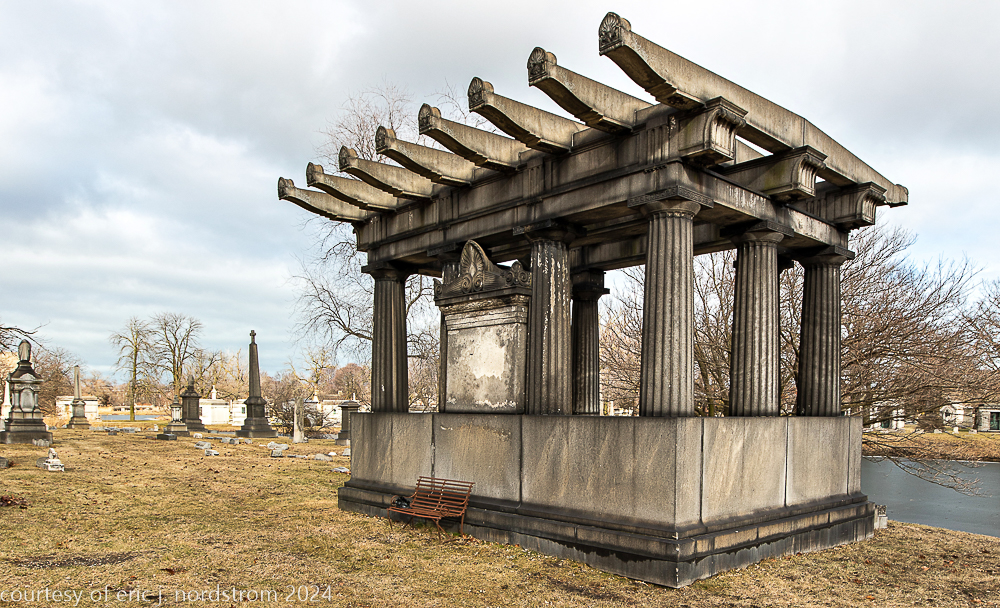
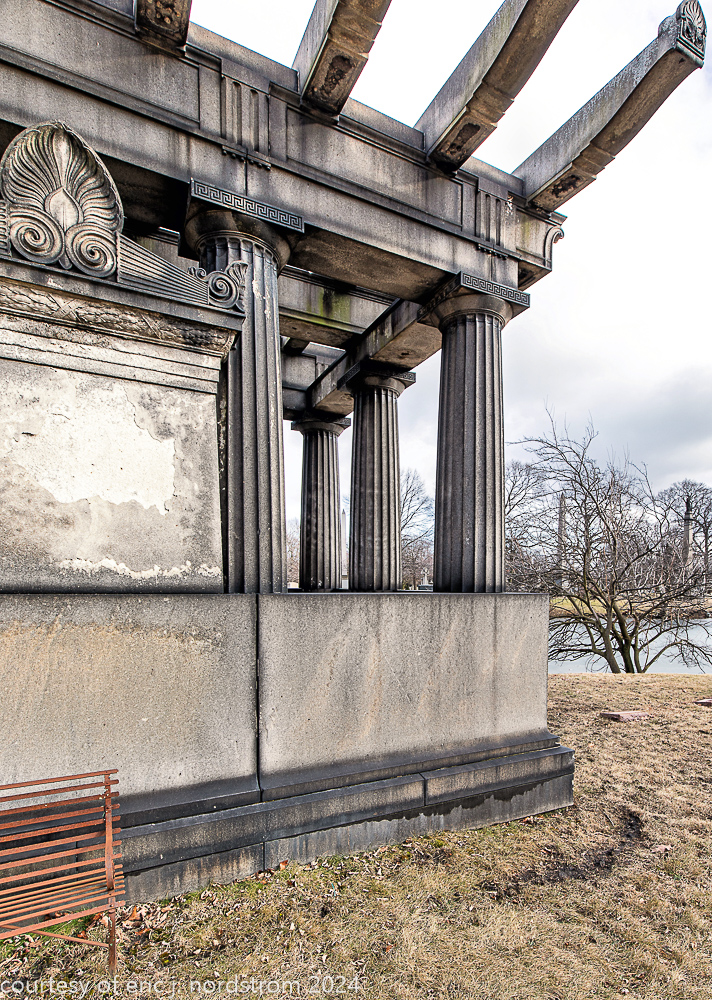
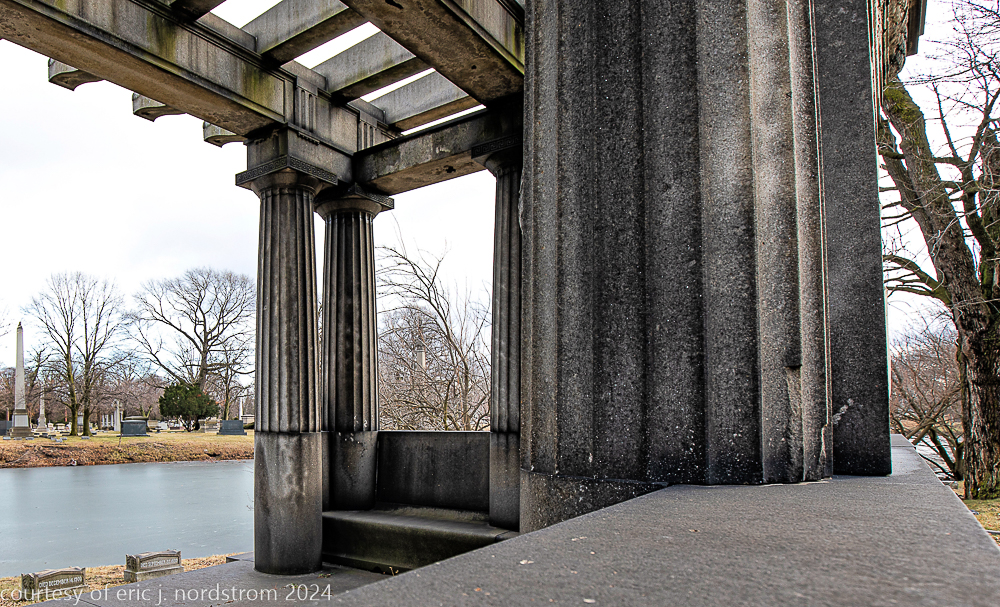
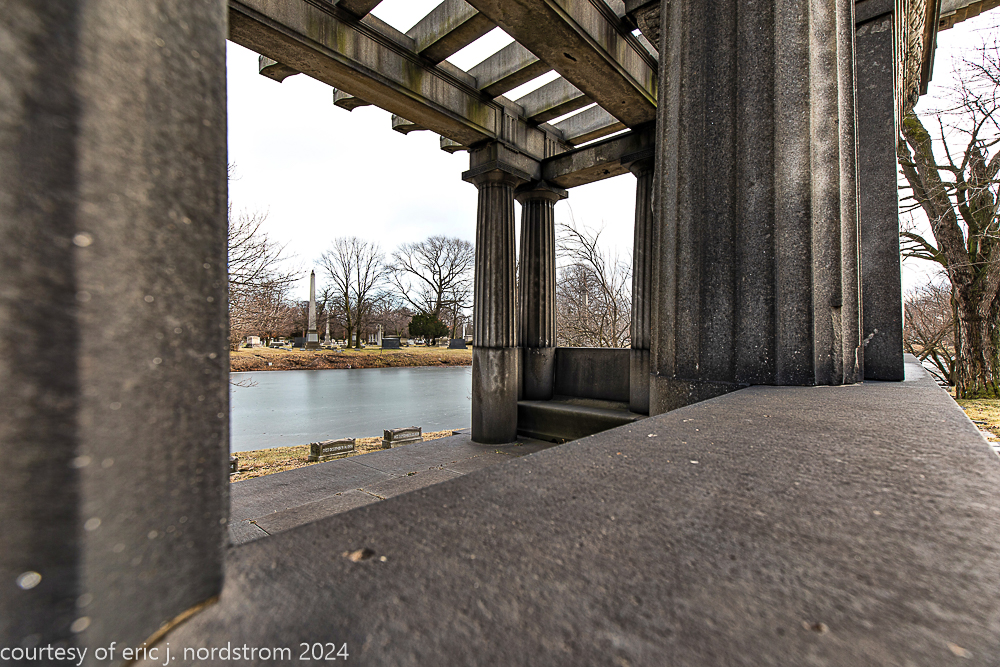
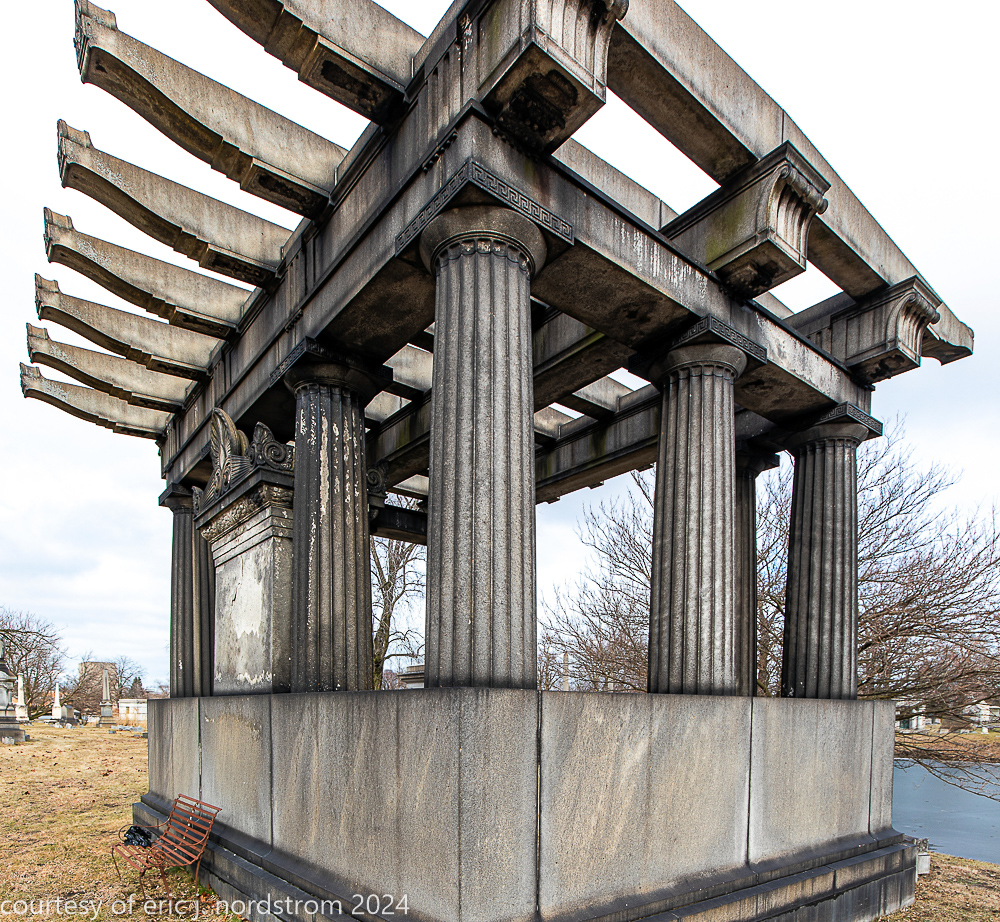
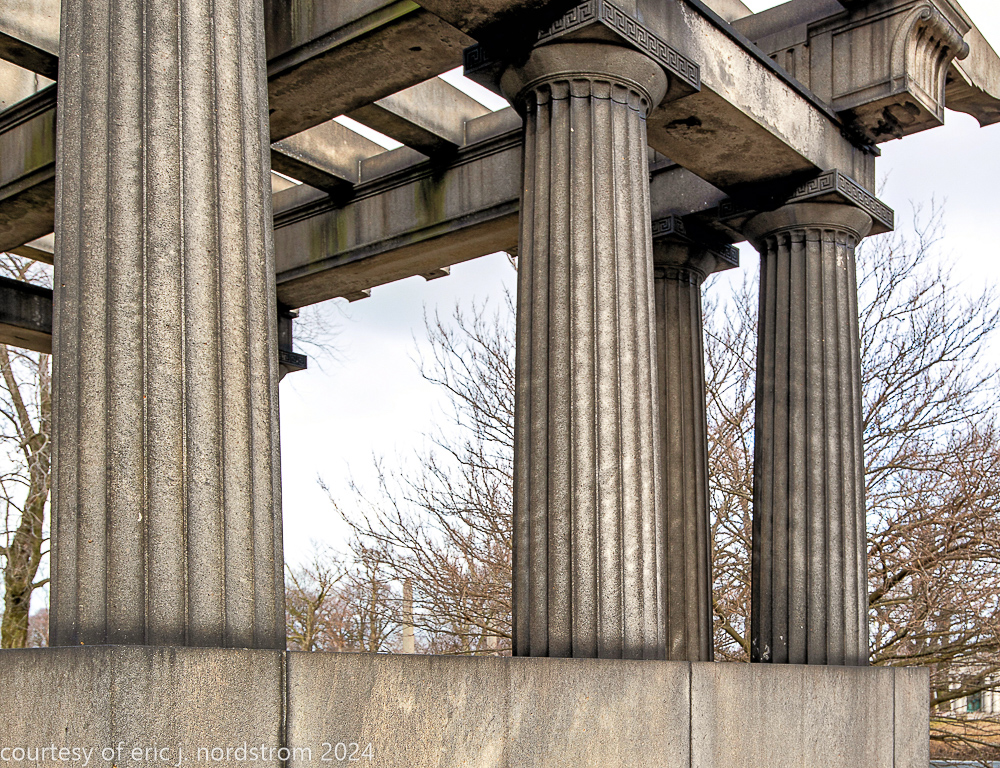
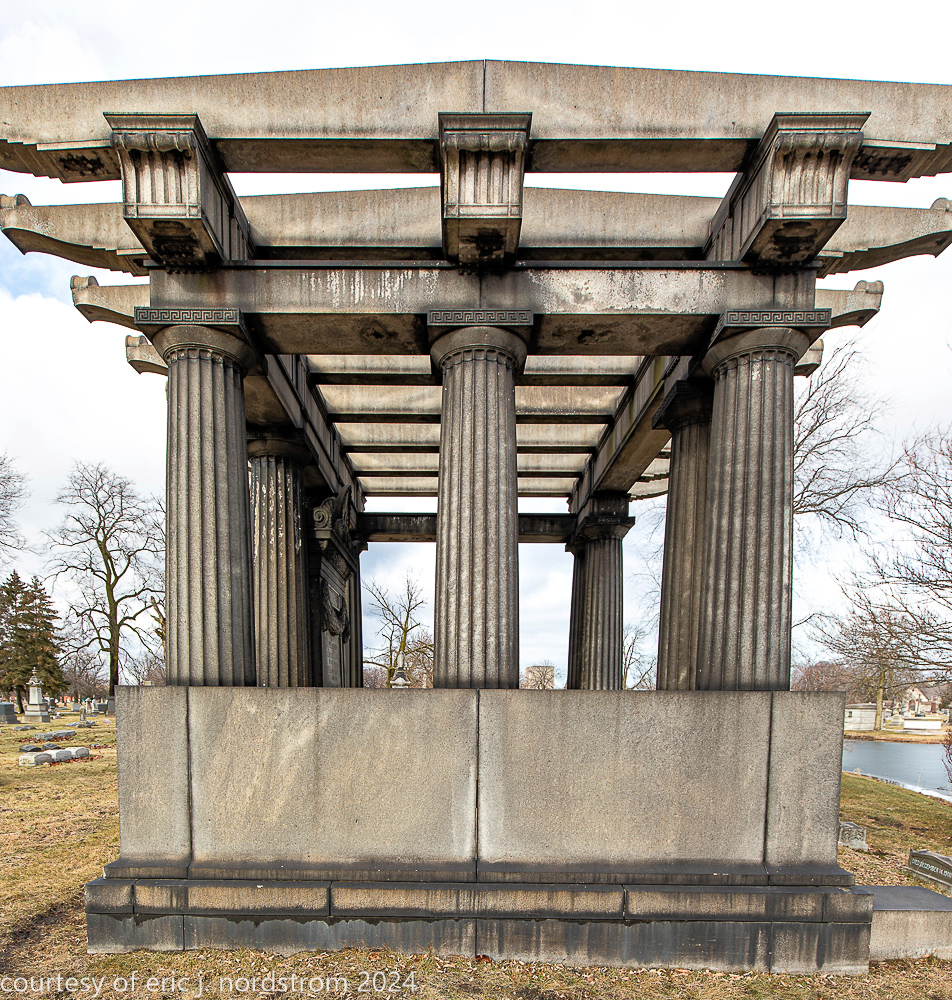
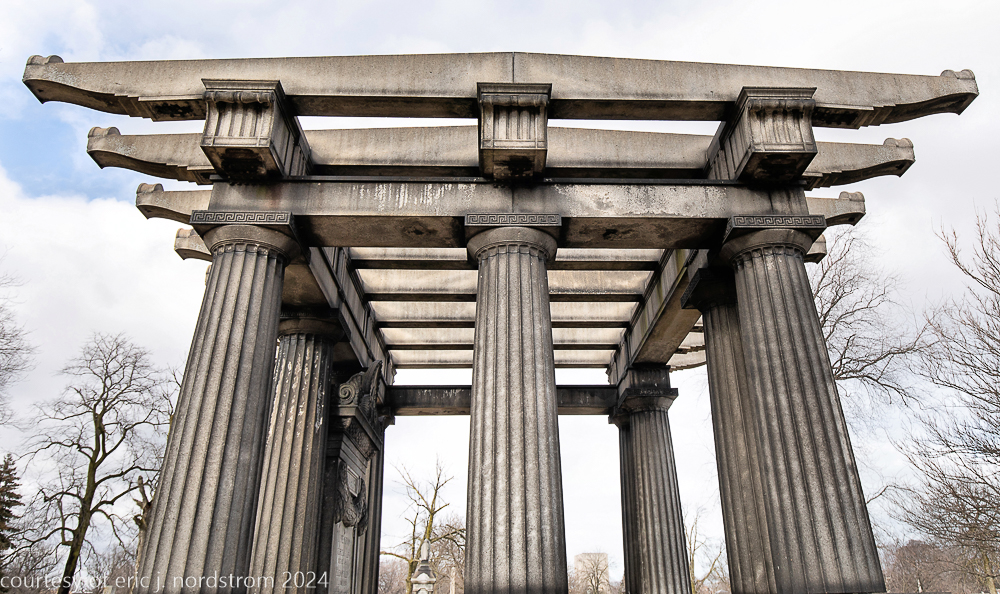
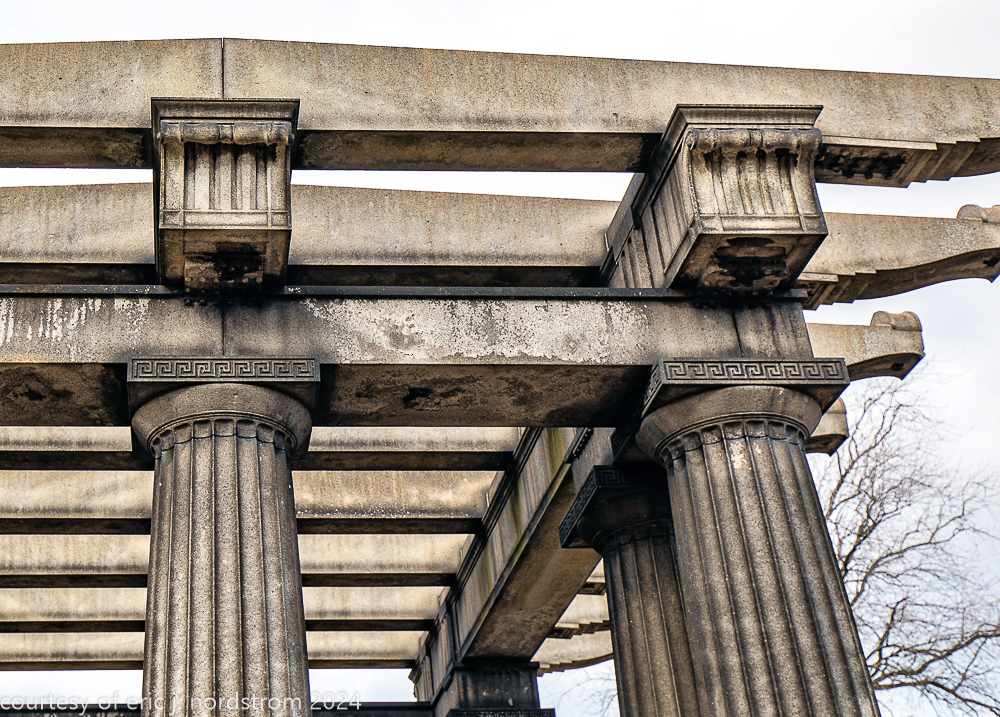
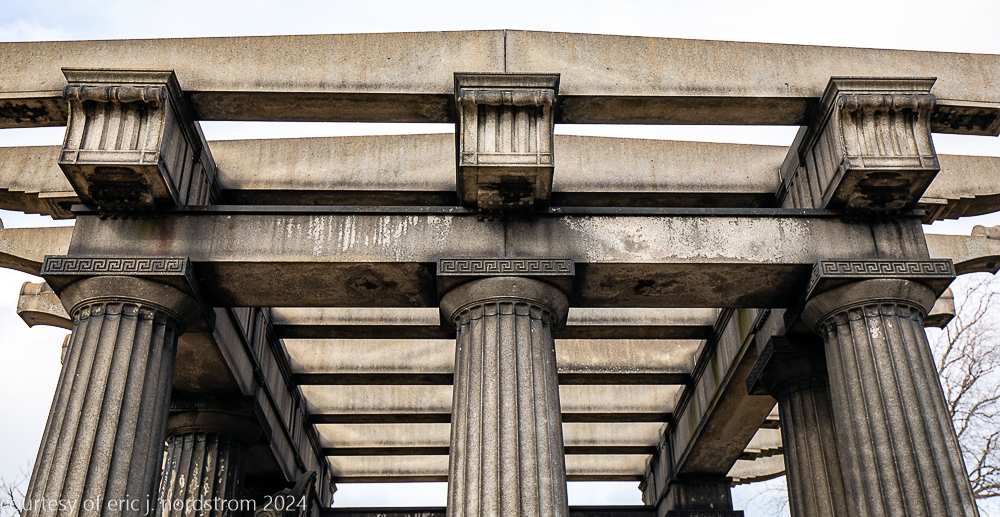
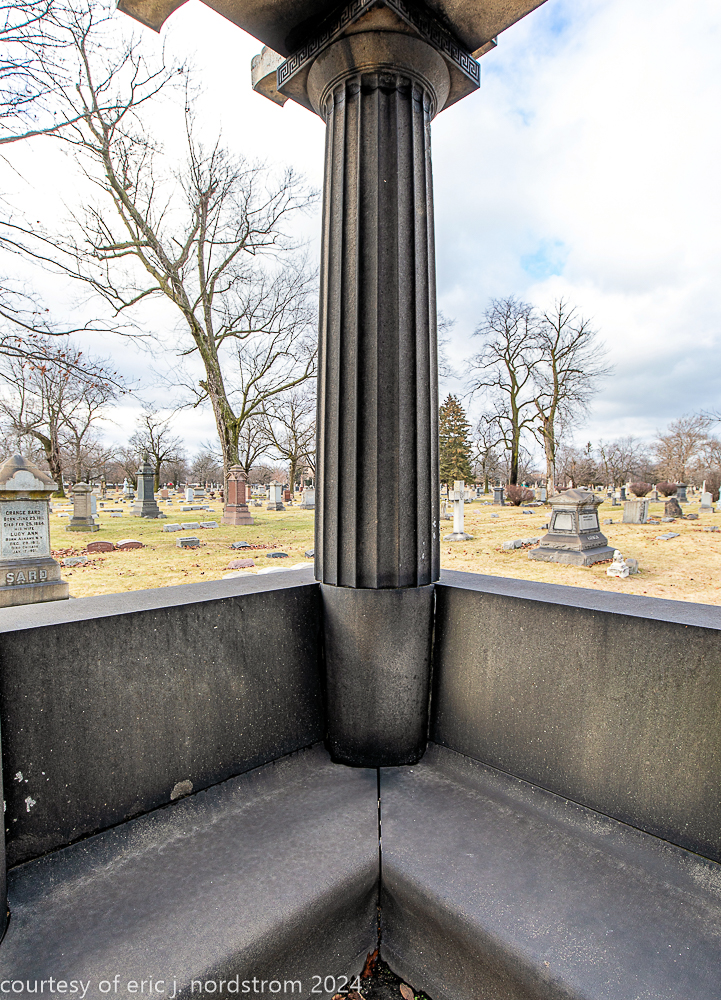
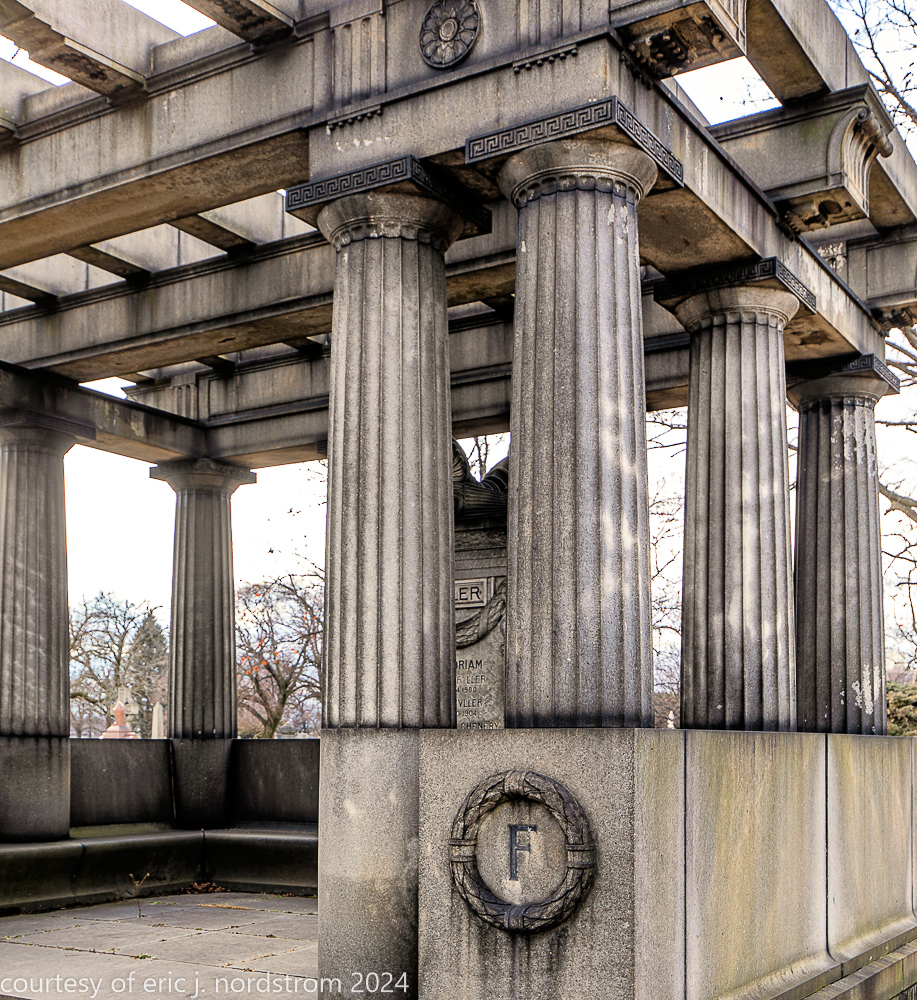
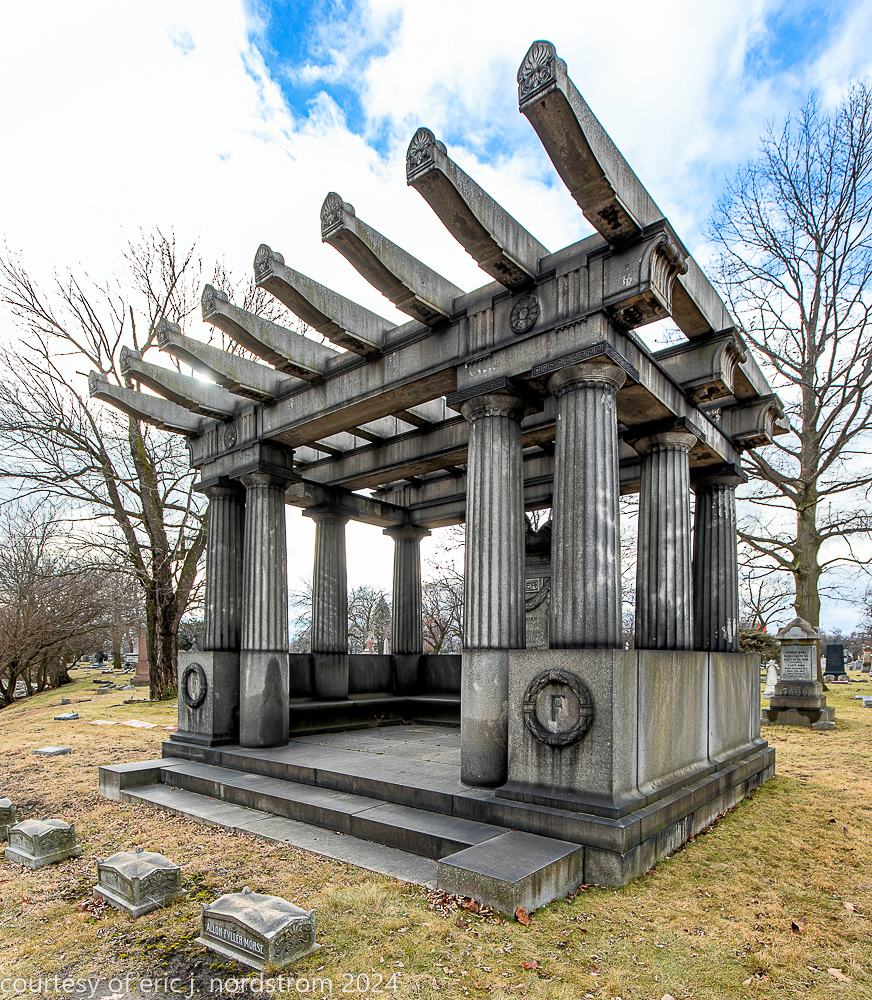
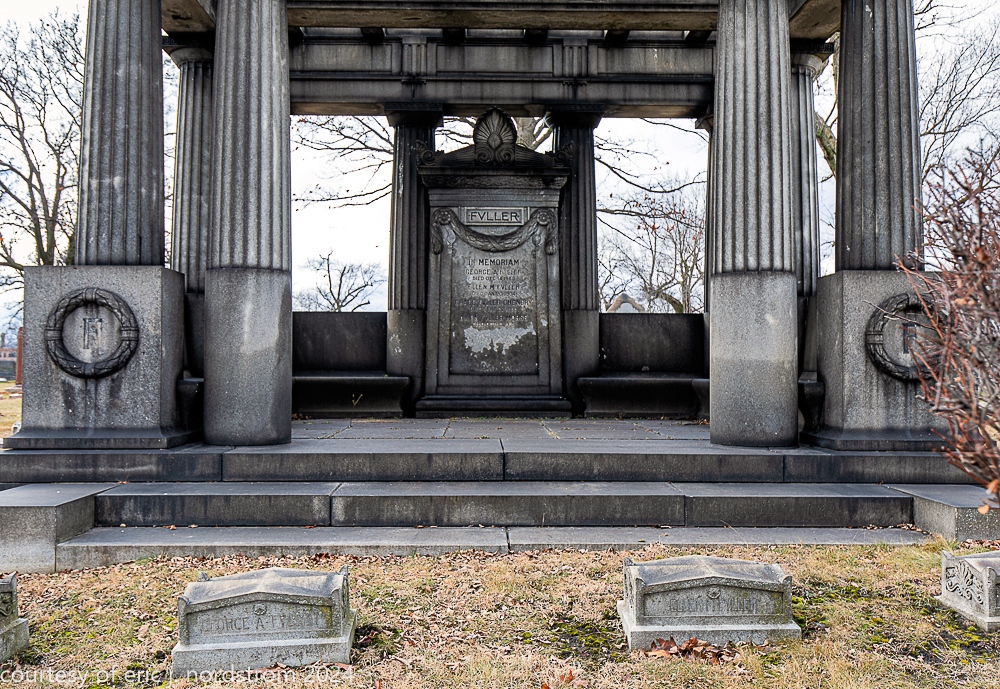
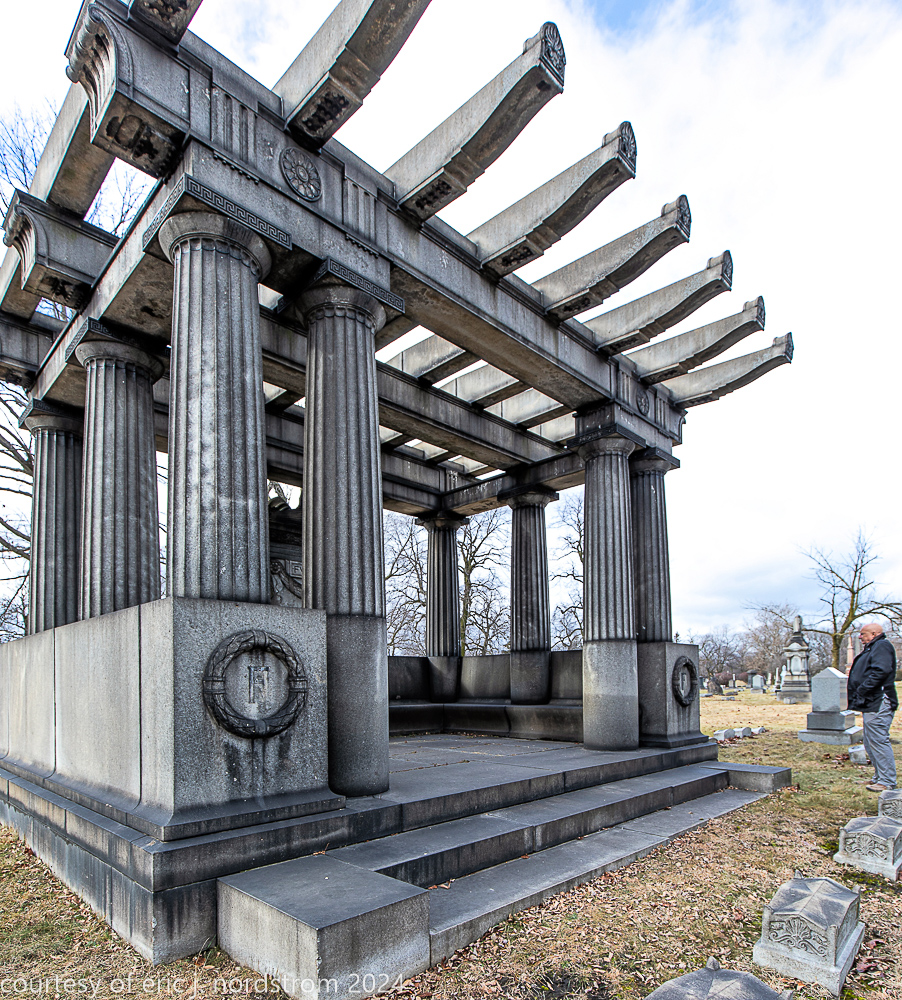
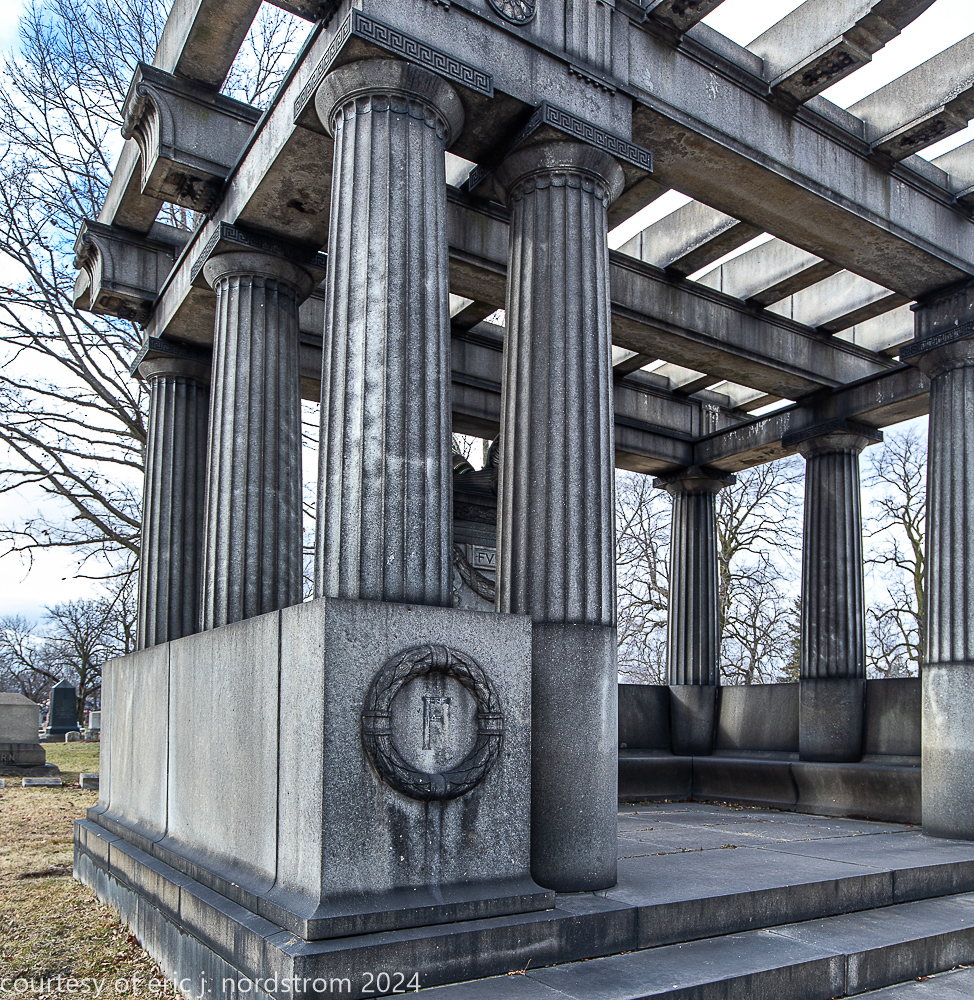
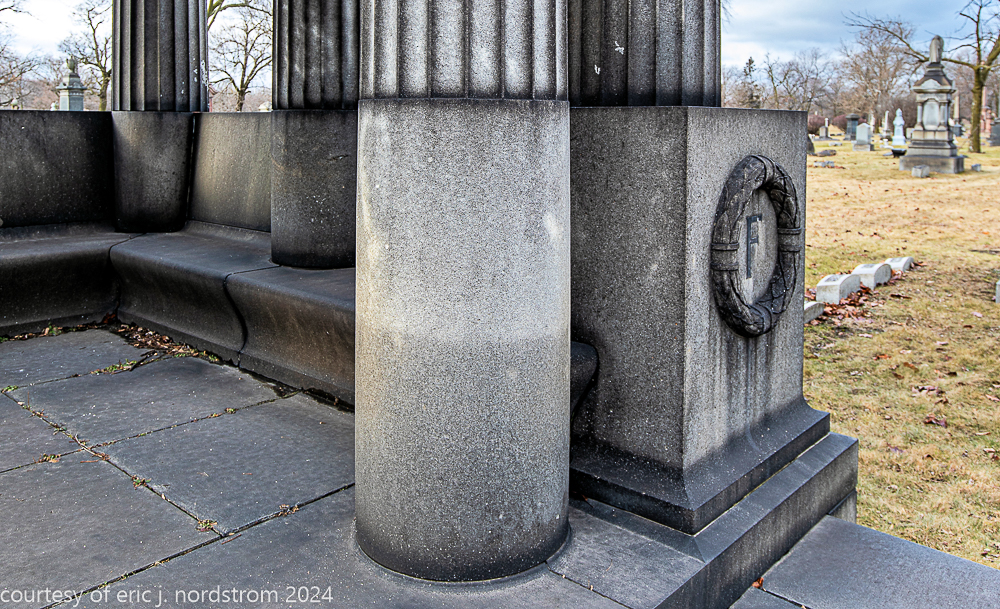
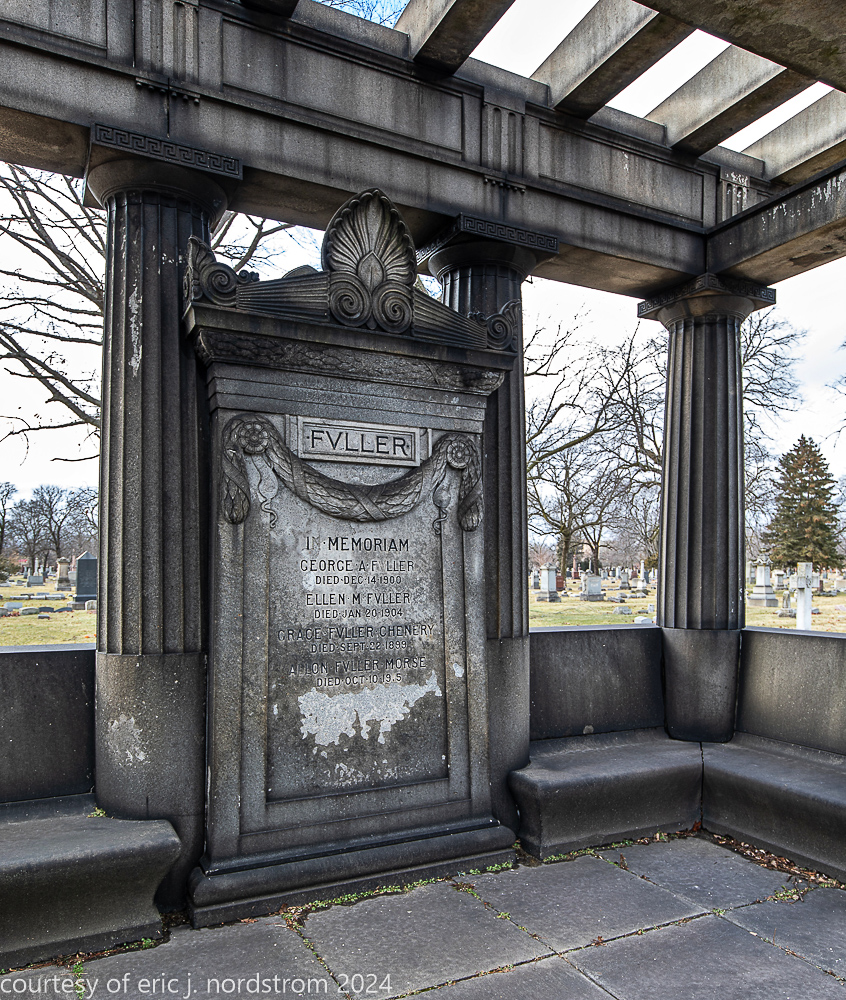
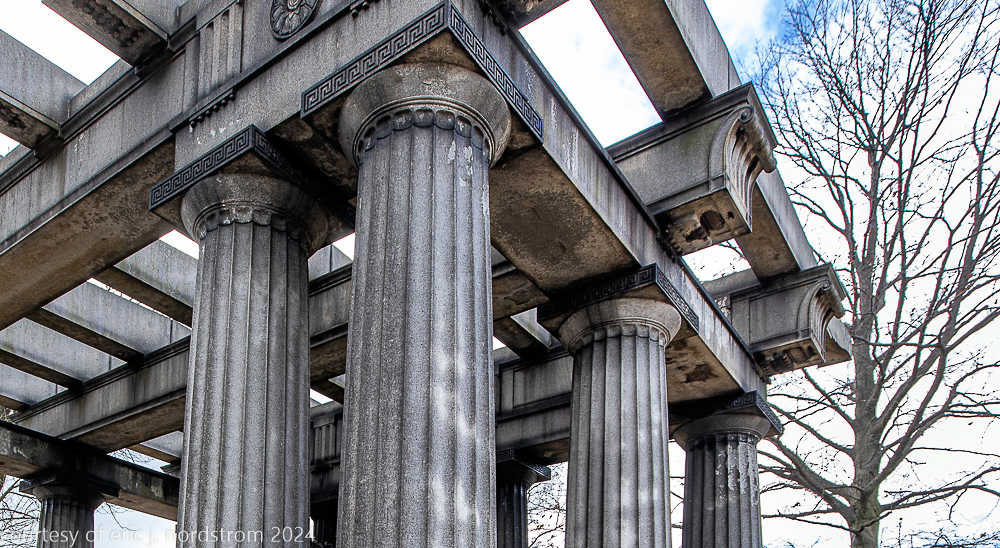
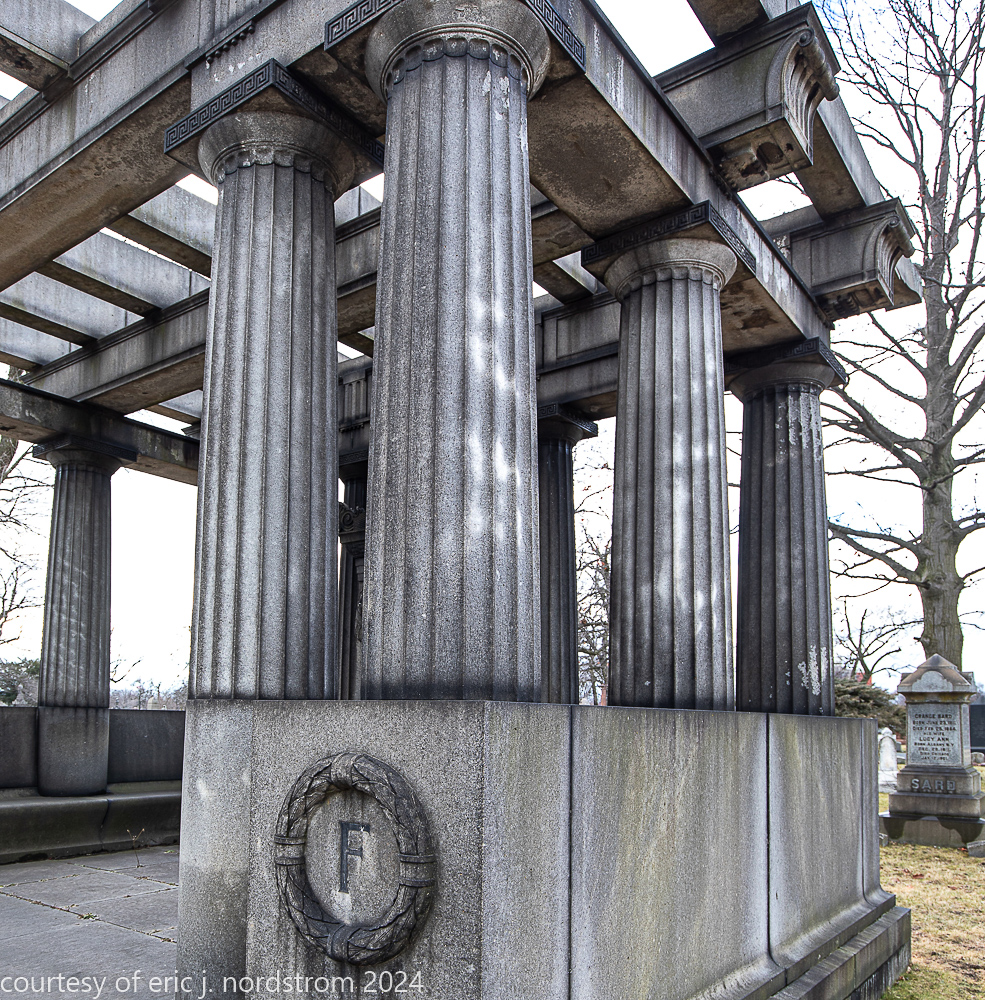
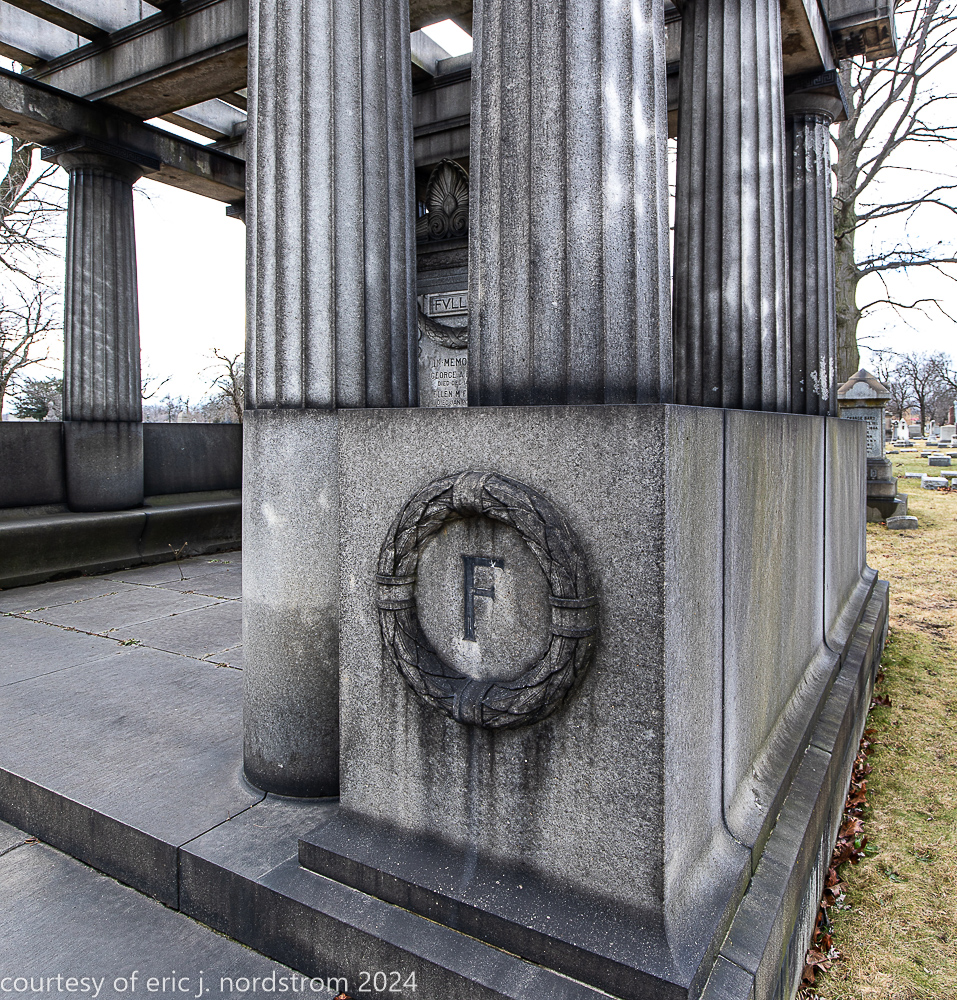
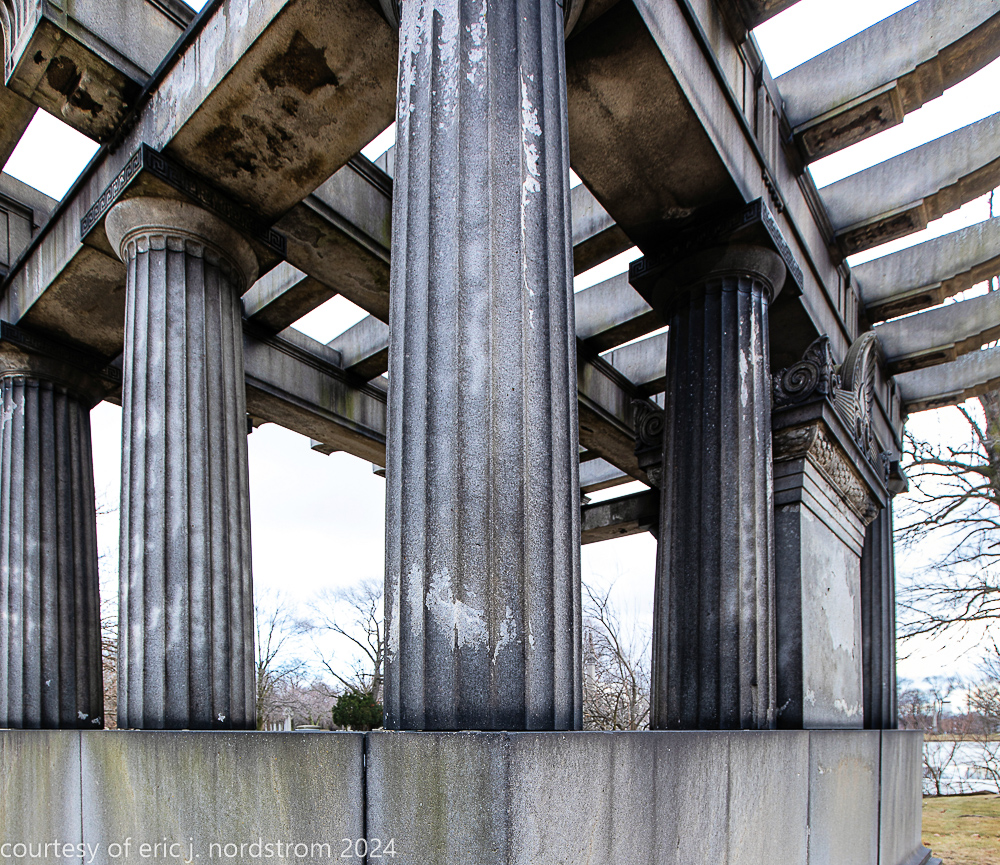
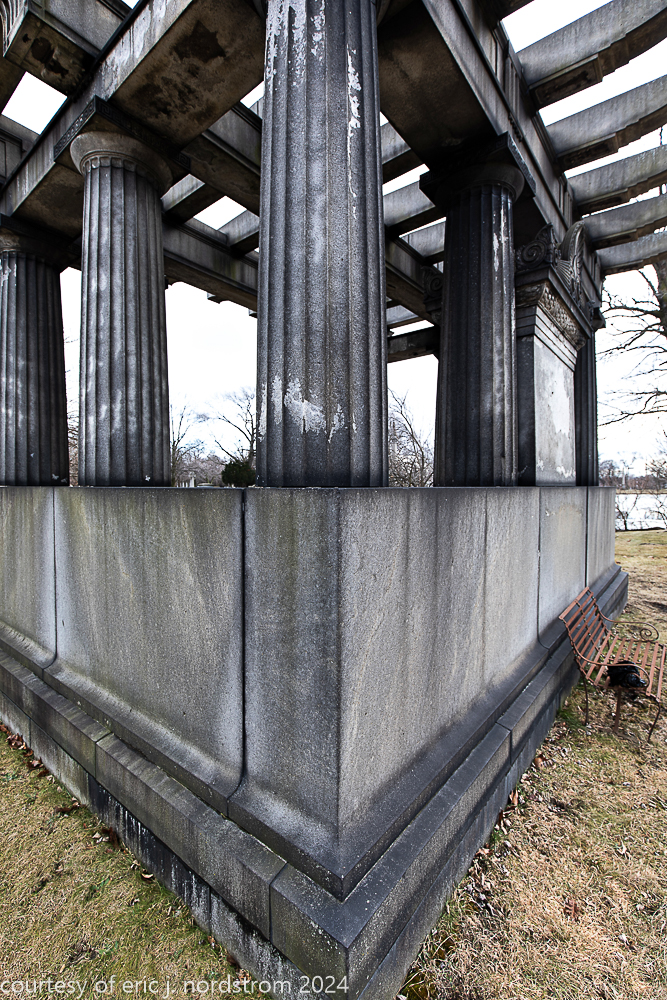
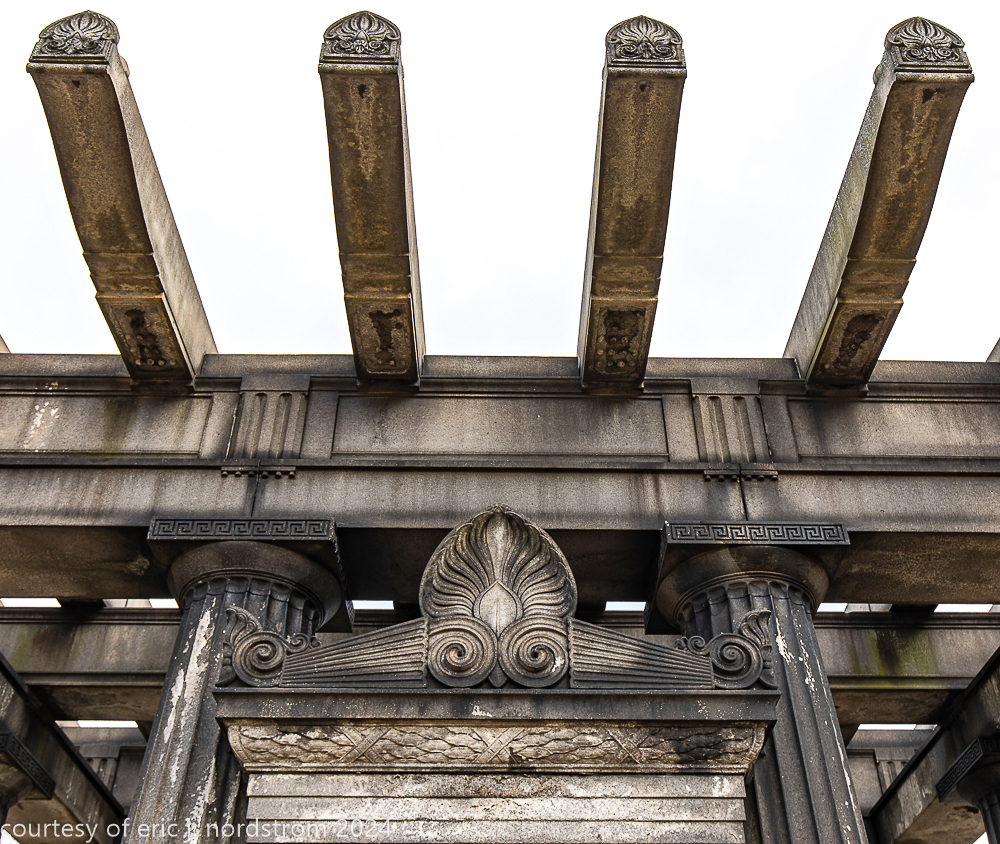
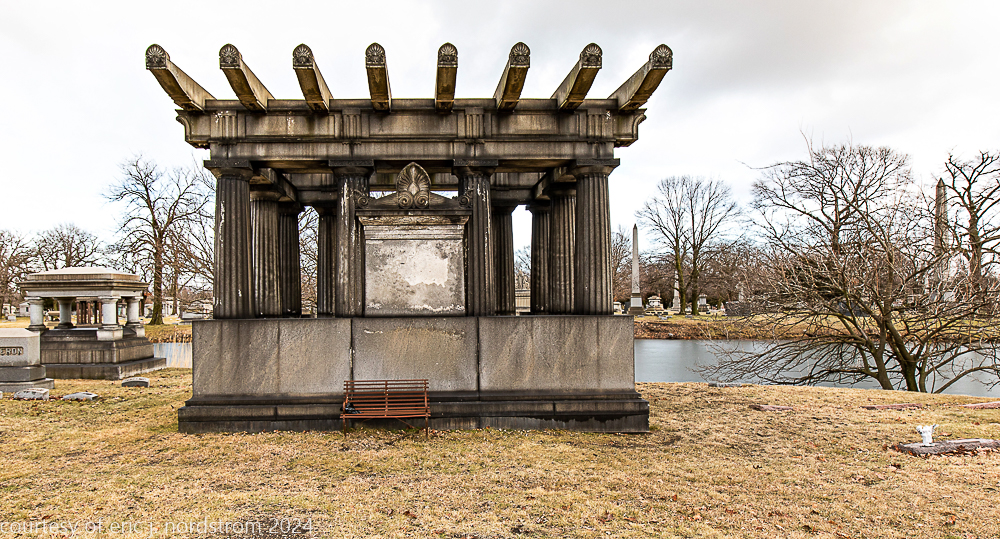
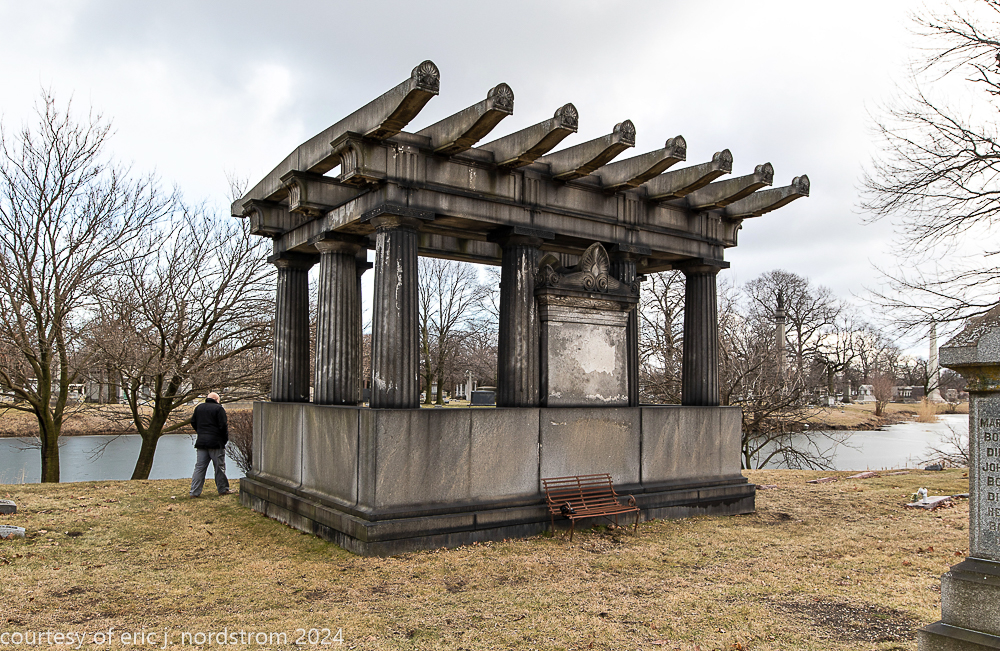

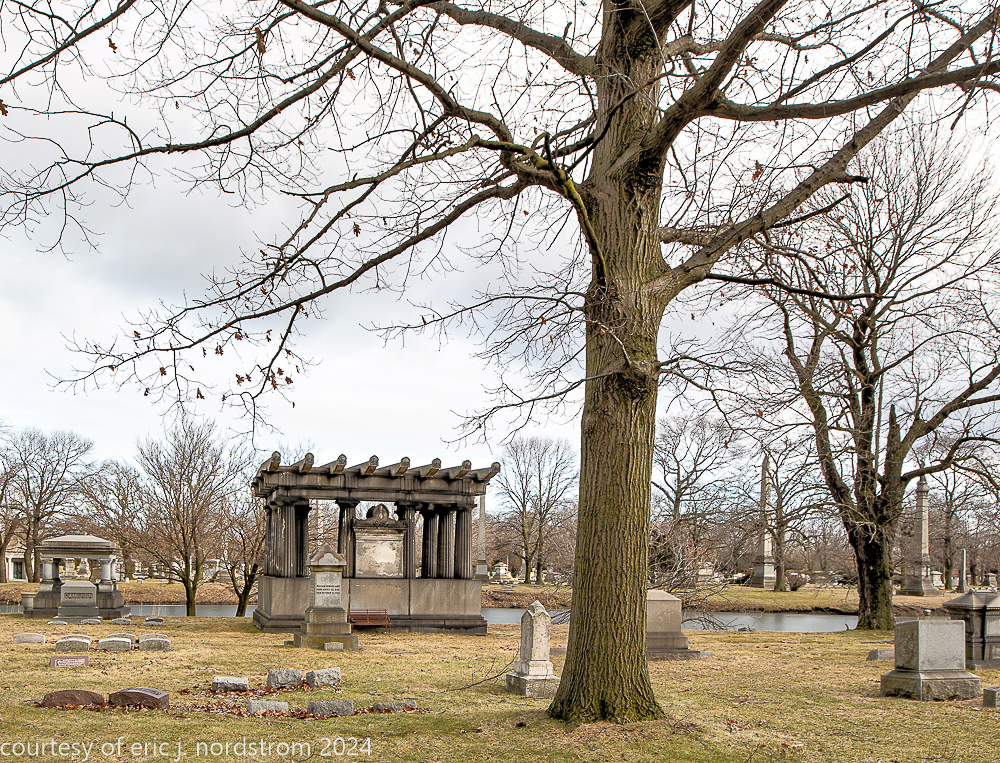














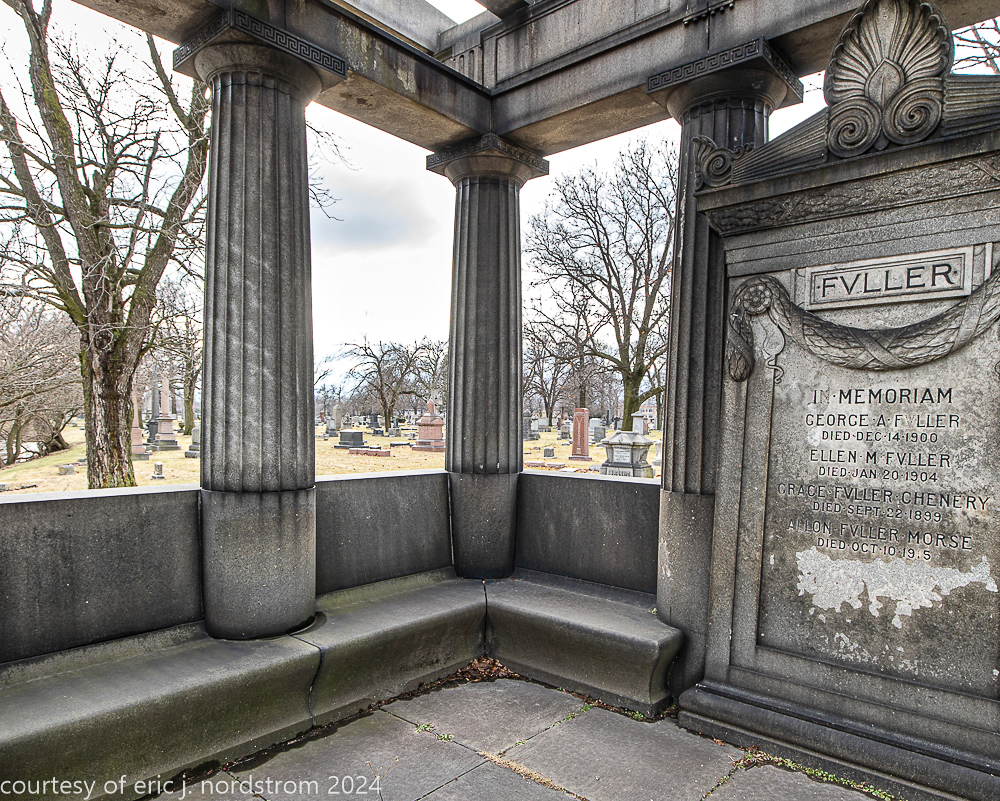









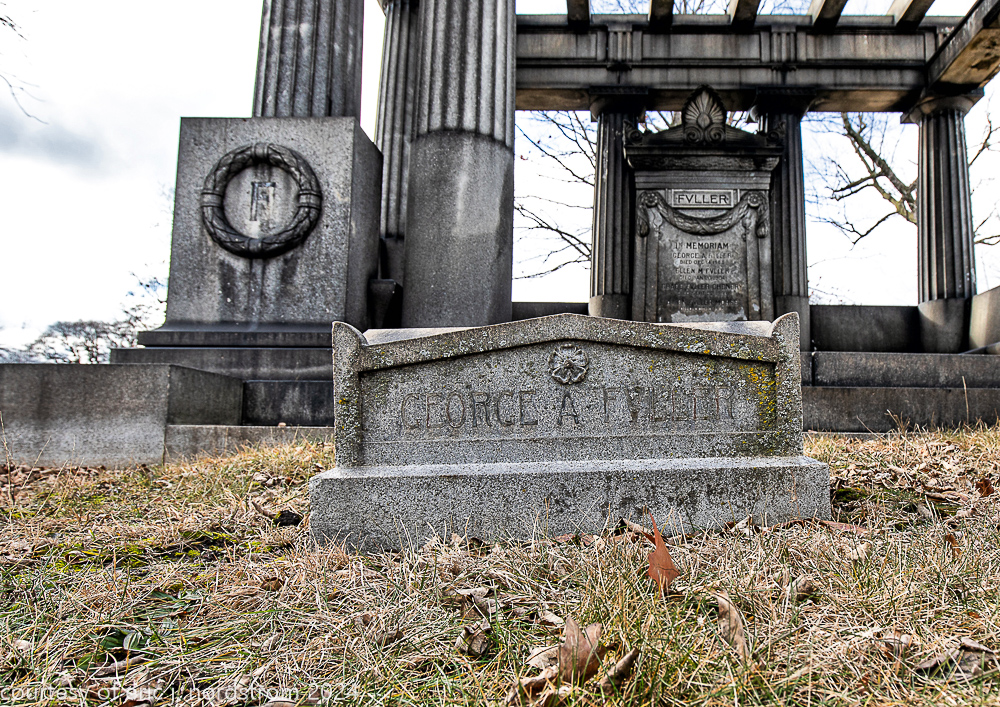
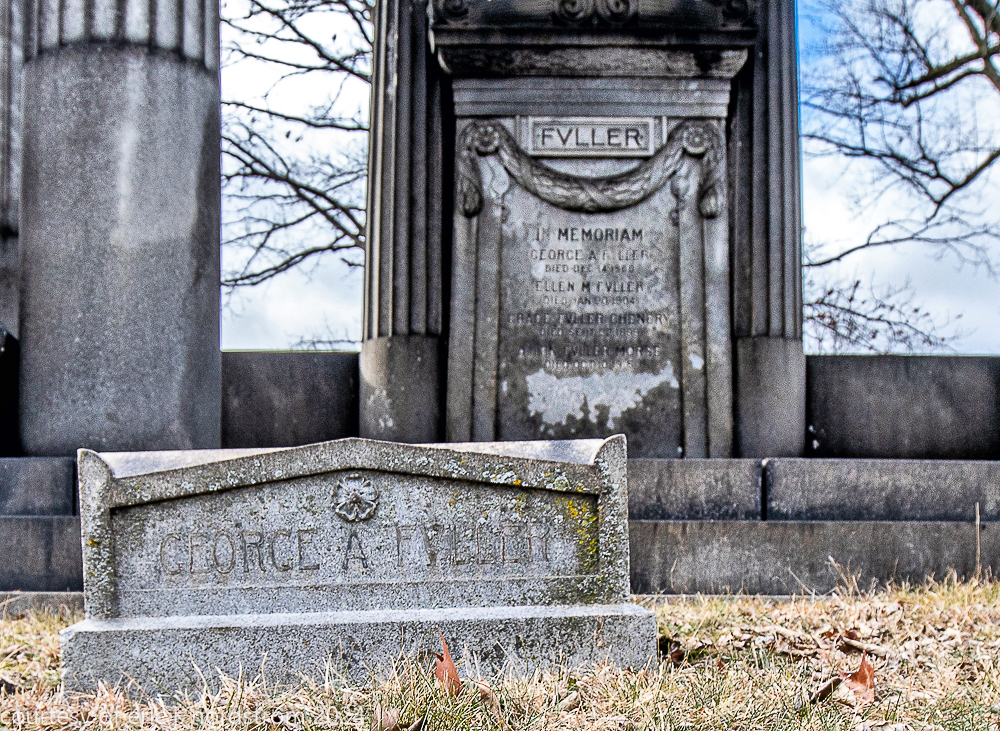




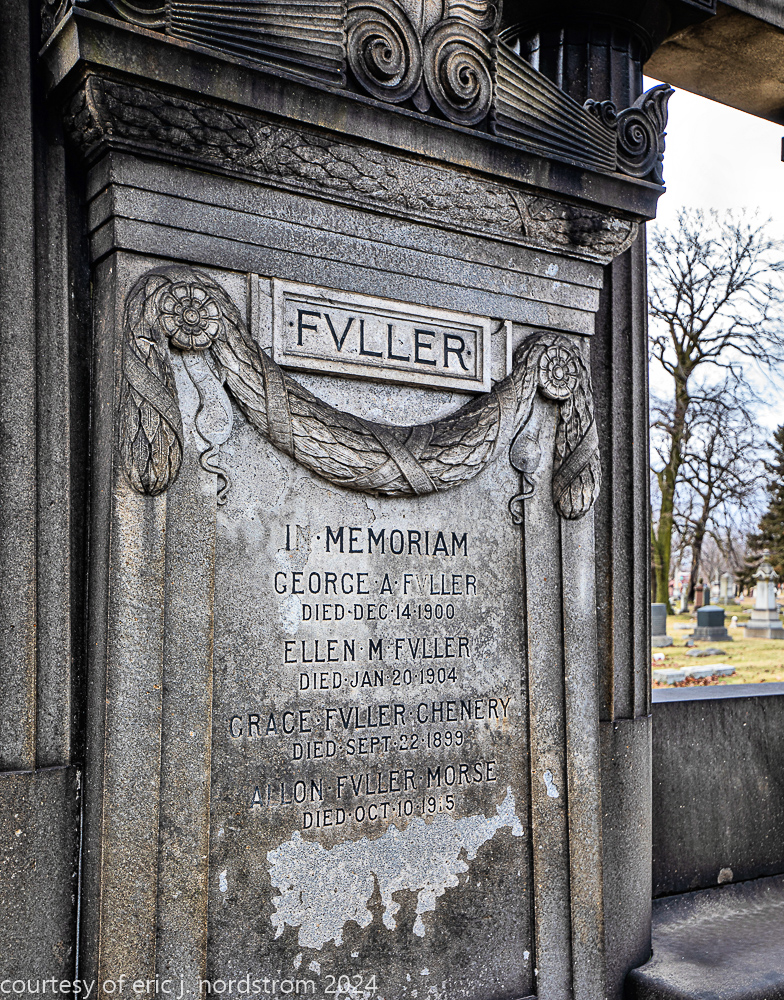
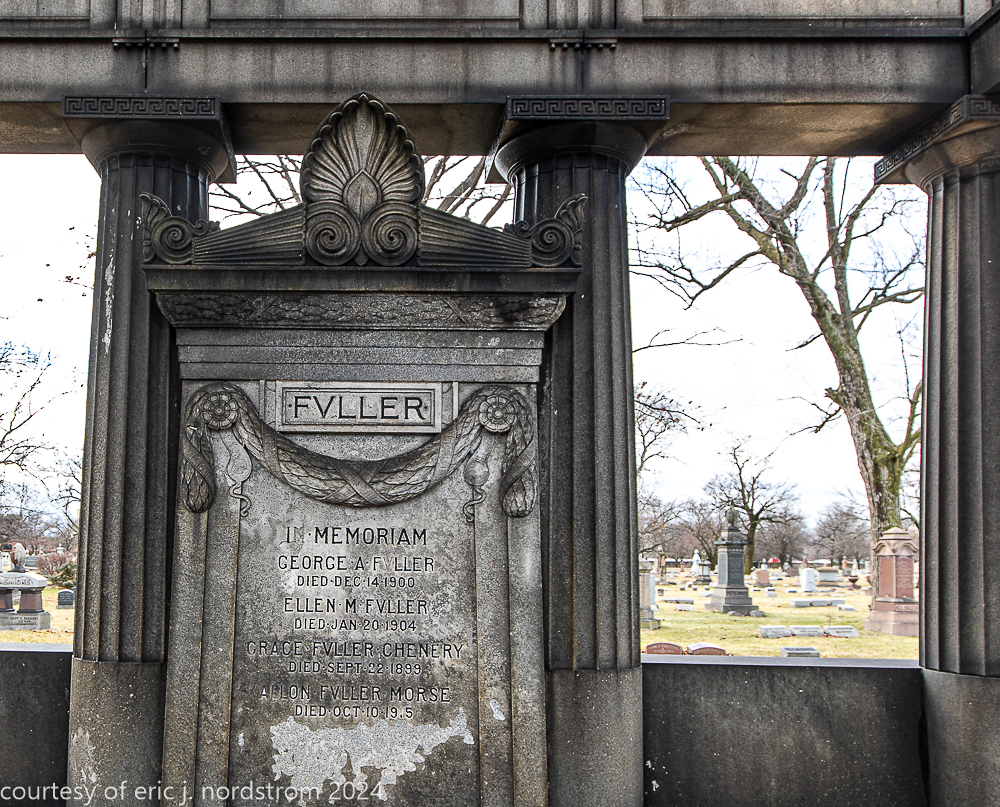









images courtesy of eric j. nordstrom and the bldg. 51 archive. all rights reserved. 2024.
This entry was posted in , Miscellaneous, Bldg. 51, Events & Announcements, Featured Posts & Bldg. 51 Feed on February 1 2024 by Eric
WORDLWIDE SHIPPING
If required, please contact an Urban Remains sales associate.
NEW PRODUCTS DAILY
Check back daily as we are constantly adding new products.
PREMIUM SUPPORT
We're here to help answer any question. Contact us anytime!
SALES & PROMOTIONS
Join our newsletter to get the latest information